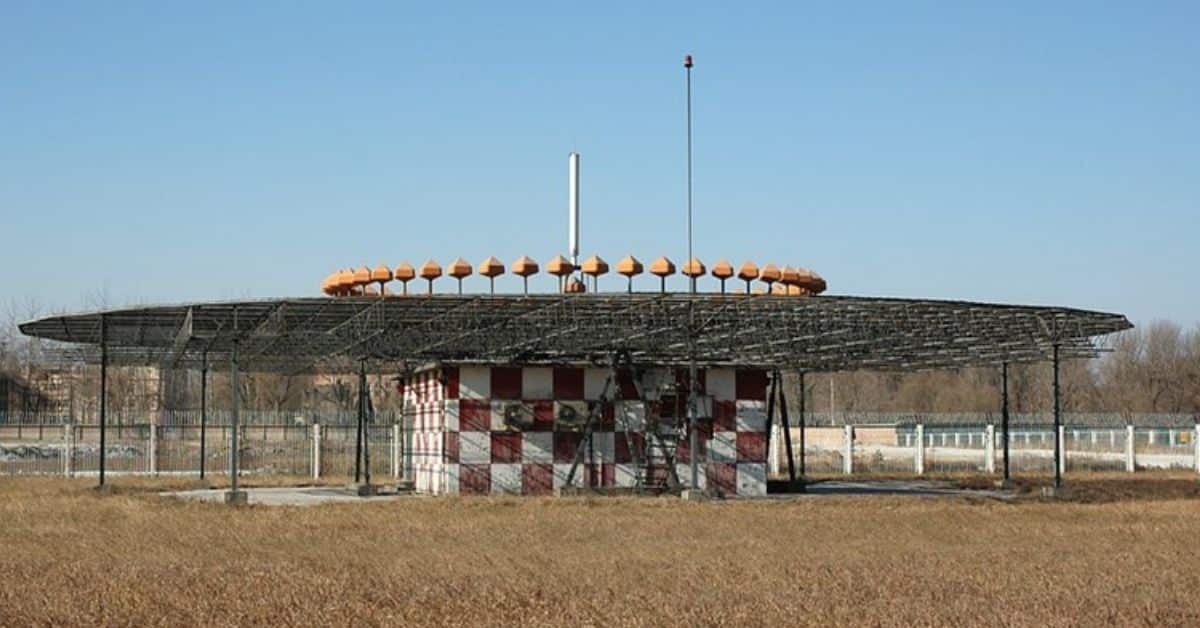
In relation to navigational aids, there are various forms of equipment utilized. The various navigational aids available have different functions and operational uses.
The key difference between a VOR and VORTAC is that the VORTAC merges the VOR and TACAN stations into one navigational aid. A VORTAC station consists of the two stations (VOR and TACAN) and their respective functions being combined into one system – VORTAC.
VOR
Short for Very High-Frequency Omnidirectional Radio Range, VOR is an aircraft navigational aid that consists of beacons that provide guidance in relation to a specified course (also referred to as a radial). The specific VOR station combined with this course provides an aircraft with positional guidance or with directions to an airport.
Operating on the high-frequency band of radio, VOR is available from 108.00 MHz through to 117.95 MHz. VOR stations are primarily intended for use by civilian aircraft.
TACAN
Short for Tactical Air Navigation, a TACAN is a military navigational aid that consists of several functions amalgamated into one unit. It is available on frequencies from 960 MHz to 1215 MHz.
Aside from being different in regards to how it is used by the military, a TACAN is a VOR with a higher degree of accuracy than that of a conventional VOR used by civilian aircraft.
It is typically more portable and compact due to the various operating environments in which it may be used. In a military environment, this may involve a TACAN being allocated to a ship for example.
Built into the TACAN is a Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) station. A DME can be also used by civilian aircraft.
VORTAC
In order to save space and reduce costs, a VORTAC station can be used to combine both the military and civilian navigational aids and components. This combination consists of a VOR, TACAN, and DME station being merged into one unit known as VORTAC.
In a VORTAC station, military aircraft utilize the TACAN function of the unit while the civilian aircraft use the VOR and DME elements. The use of VORTAC stations has increased in airspaces where there is a mutual presence of both military and civilian aircraft. In a modern-day context, shared airspace is ubiquitous in this sense.
VORTACS have numerous benefits over conventional, separate navigational aids. The primary advantage is the ability to merge the various stations into one unit. Like stated previously, VORTACs also offer dual navigation services for both military and civil aircraft.
In the United States and Europe, most VORs and TACANs are in fact VORTAC stations.
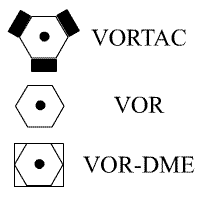
VOR vs VORTAC Symbols
Aviation navigational aids are commonly assigned symbols for visual identification purposes. The following symbols are assigned to VORTAC, VOR, and VOR-DME symbols respectively.
3-Letter Designations
All active VOR, DME, TACAN, and VORTAC stations are assigned unique 3-letter codes for designation and identification purposes. These 3-letter codes are officially registered with the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO). Some examples would be Dublin (DUB), Bovingdon (BNN), and Charles De-Gaulle (CDG).
Read More:
Why Are Airport Runways So Expensive?

After visiting more than 60 countries, I have probably been on every type of plane there is and visited countless airports. I did my very first international solo trip to South Africa at the age of only 16 and haven’t really stopped traveling since.
Despite the adventurous travel itch, I do have a nerdy side as well – which is satisfied by writing about all things aviation “too boring” for my regular travel blog.